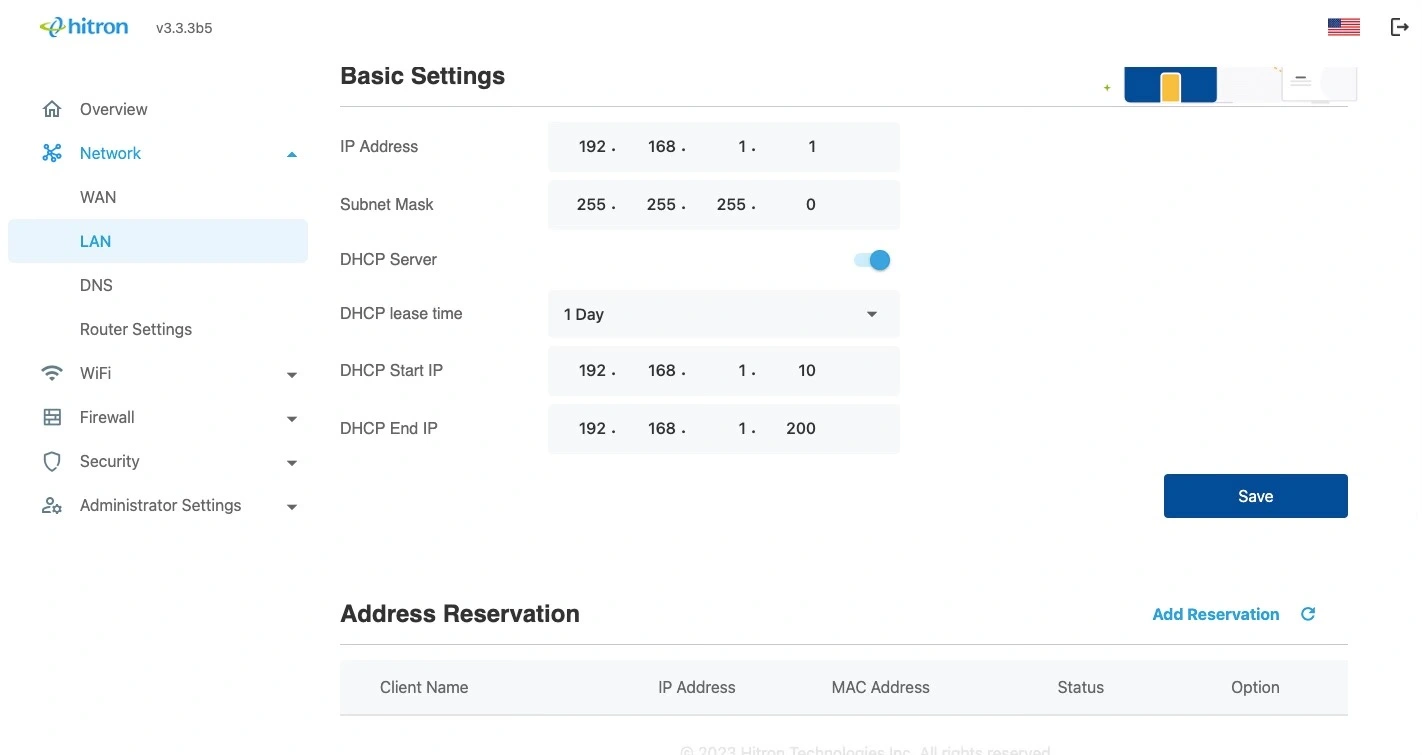
DHCP explained
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, or DHCP, defines the process by which IP addresses can be assigned to computers and other networking devices automatically, from another device on the network. This device is known as a DHCP server, and provides addresses to all the DHCP client devices. In order to receive an IP address via DHCP, a computer must first request one from the DHCP server (this is a broadcast request, meaning that it is sent out to the whole network, rather than just one IP address). The DHCP server hears the requests, and responds by assigning an IP address to the computer that requested it. If a computer is not configured to request an IP address via DHCP, you must configure an IP address manually if you want to access other computers and devices on the network.
By default, the ARIA3411 is a DHCP client on the WAN (the CATV connection). It broadcasts an IP address over the cable network, and receives one from the service provider. By default, the ARIA3411 is a DHCP server on the LAN; it provides IP addresses to computers on the LAN which request them.
Buttons for the activation/deactivation of LAN DHCP:
Use these buttons to activate/deactivate the DHCP server function for private LAN IP addresses. When the DHCP server is activated, LAN IP addresses and DNS information are assigned to the devices.
DHCP lease time
“DHCP lease time” refers to the length of time for which a DHCP server allows a DHCP client to use an IP address. Usually, a DHCP client will request a DHCP lease renewal before the lease time is up, and can continue to use the IP address for an additional period. However, if the client does not request a renewal, the DHCP server stops allowing the client to use the IP address. This is done to prevent IP addresses from being used up by computers that no longer require them, since the pool of available IP addresses is finite.
The DHCP least time specification defines how long a certain IP address is reserved for a client. The client must report to the server again before then and apply for an “extension”. If the client does not respond, the address will become free and can be reassigned to another (or the same) client.
DHCP Start IP
Displays the first available LAN IP address assigned by the LAN DHCP.
DHCP End IP
Displays the last available LAN IP address which is assigned by the LAN DHCP. The number of IP addresses between the DHCP start IP and the DHCP end IP determines the size of the DHCP IP address pool.
IP-Address
The IP address is the LAN IP address of the gateway. Devices connected to your broadband service require DHCP IP addresses that belong to the same subnet as the private LAN IP address of your broadband service.
Subnet mask
This field defines the size of the LAN subnet used by the DHCP server of your services for private LAN addressing.
LAN Settings (Web GUI)
Address Reservation
The Address Reservation function allows you to reserve IP addresses for your devices.
Step 1: Click the Add Reservation button to enter the Address Reservation setting page.
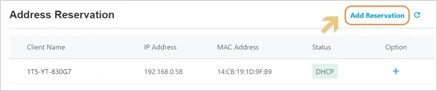
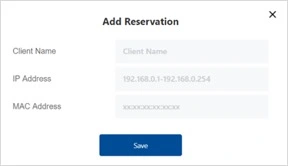
You can either make an IP address reservation from a current connected device by click the + from the option or create new entries for the devices that haven’t join the network.
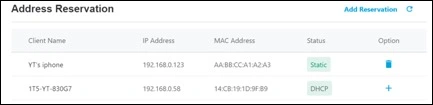
Step 2: Click Save to save your settings.